Total Cost Curve for a Typical Firm
Draw the marginal-cost and average-total-cost curves for a typical firm. In the long run the firm can examine the average total cost curves associated with varying levels of capital.
Solved Figure 13 7 Figurc 1 Figurc 2 Figure 3 Figure Refer Chegg Com
40With fixed costs of P400 a firm has average total costs of P3 and average variable costs of P250.
. Here are a number of highest rated Lrac Curve Of The Firm pictures upon internet. Define diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise. 41The reason the marginal cost curve eventually increases as output increases for the typical firm is because.
Whenever marginal cost is greater than average total cost average total cost is rising. Define economies of scale and diseconomies of scale and explain why they might arise. Its marginal cost is MC 302 - 1200 910.
D resource prices rise as output is increased. And 3 whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost average total cost is declining. Its submitted by presidency in the best field.
This isnt necessarily always the case- the total cost curve could be linear in quantity for example- but is fairly typical for a firm for reasons that will be explained. Explain why the curves have the shapes that they do and why they intersect where they do. Explain why the curves have the shapes that they do and why they cross where they do.
How much profit will this firm make if it is applying the profit maximizing rule. Whenever marginal cost is greater than average total cost average total cost is rising. If the industrys demand curve is described by P 195 - 4Q.
Under what conditions will a firm shut down temporarily. The total cost curve is generally bowed upwards. 1 marginal cost is rising.
TC Q Q 15Q 225. Average variable cost AVC is calculated by dividing variable cost by the quantity produced. There are various types of cost curves all related to each other.
For a perfectly competitive firm producing the profit-maximizing quantity the average total cost is 10 and the average variable cost is 8. At that level of output show on your graph the firms total revenue and total costs. Average total cost ATC is calculated by dividing total cost by the total quantity produced.
Draw the cost curves for a typical firm. 2 average total cost is U-shaped. A is 400.
The total cost curve is upward sloping ie. The information on total costs fixed cost and variable cost can also be presented on a per-unit basis. The long-run average cost curve is a type of lower boundary of the short-run cost curves.
Of diseconomies of scale. In a free market economy productively efficient firms use these curves to find the optimal point of production where they make the most profits. It has three main features.
A monopoly firms total cost is. Does a firm s price equal marginal cost in the short run in the long run or both. B is 40.
A firms total cost curve is TV 03 - 60Q2 9100 150. We identified it from well-behaved source. In economics a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced.
D can not be. And 3 whenever marginal cost is less than average total cost average total cost is declining. Chapter 13 Problem 6RQ is solved.
MC 20 15 O a 2025 O b 1575 Oc 279 O d. C is 10. The average total cost curve is typically U-shaped.
Does a firm s price equal the minimum of average total cost in the short run in the long run or both. This can be understood most easily by thinking of a series of short-run average total cost curves each one for a different level of the fixed input capital as shown in Figure 831. This simply reflects the fact that it costs more in total to produce more output.
3775 O e 506. 2 average total cost is U-shaped. At that level of output show on your graph the firms total revenue and total costs.
Draw an Average Total Cost curve in the short run and long run for a small factory a medium factory and a large factory. At the long - run equilib level of output this firm s total cost. Figure 6 shows the marginal-cost curve and the average-total-cost curve for a typical firm.
We believe this nice of Lrac Curve Of The Firm graphic could possibly be the most trending subject in. Define economies of scale and explain why they might arise. Explain the relationship between Marginal Cost and.
At the point of intersection of MR and MC when we extend the line on to the x-axis we can plot the profit maximizing output Qmax. Draw the marginal-cost and average-total-cost curves for a typical firm. Answer to Suppose a firms short run total cost curve can be expressed as TCQ50Q.
For a given price explain how the firm chooses the level of output that maximizes profit. Explain how a competitive firm chooses the level of output that maximizes profit. Draw the cost curves for a typical firm.
The firms fix cost is ОО O 150 0910 120 Question 6 The firms variable cost is O VC - 03-6002 9100 O VC Q2 - 600 910 OVC - 6002 910Q 150 OVC 302 - 1200 The firms average total cost O ATC 910 ATC 150 O ATC Q2 - 60Q 910 150Q O ATC. Answer- Figure 6 shows the marginal-cost curve and the average-total-cost curve for a typical firmIt has three main features. ATC average total cost.
Qmax profit maximizing output. Lrac Curve Of The Firm. 1 marginal cost is rising.
100 11 ratings for this solution. 16 The graph depicts the average total cost curve for a perfectly competitive firm. Qmax profit maximizing output.
Step 1 of 4. Under what conditions will a firm exit a market. At the point of intersection of MR and MC when we extend the line on to the x-axis we can plot the profit maximizing output Qmax.
A firm will produce output until its marginal revenue equals its marginal cost. The average- total-cost curve is U-shaped because the firm initially is able to spread out fixed costs over additional units but as quantity increases it costs more to increase quantity further because an important input is limited. This firms short-run average total cost curve can be expressed as.
Draw the marginal-cost and average-total-cost curves for a typical firm. ATC average total cost. Are market supply curves typically more elastic in the short run or in the long run.
A firm will produce output until its marginal revenue equals its marginal cost. As industry output contracts each firms long-run average total cost curve shifts upward. Four possible short-run average total cost curves for Lifetime Disc are shown in Figure 89 Relationship Between Short-Run and Long-Run Average Total Costs for quantities of capital of 20 30 40 and 50 units.
Answer In Microeconomics For Julius 203197
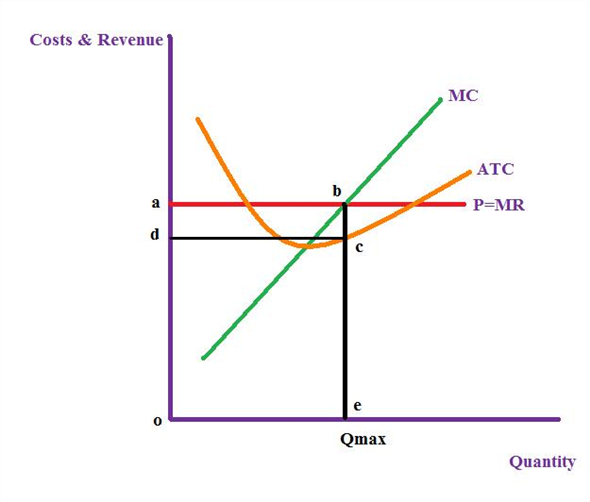
Solved Draw The Cost Curves For A Typical Firm For A Given Price Chegg Com
No comments for "Total Cost Curve for a Typical Firm"
Post a Comment